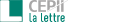While Chinese industrial subsidies have been one of the key drivers of international trade tensions, the details of the phenomenon itself are often overlooked. Reviewing the existing datasets and methodologies used to assess Chinese public supports, this Policy Brief tries to bring more clarity on what is known, and what is not. The most frequently used datasets in the literature are dated and/or largely incomplete, and find limited industrial support compared to more specific analyses. To further complicate things, the new development model pursued by the current leadership seems to champion the idea of “guiding” economic entities to align with Party-State objectives, which, by diffusing public intervention throughout the economy, makes it more difficult to assess the scale of subsidies. The Chinese authorities highly structured and detailed communication and policy planning offers alternative metrics to assess the distribution and evolution of public support to the industry, enabling a complementary approach to triangulate the actual subsidies to industrial production in China. François Chimits
>>> |
Created mainly to promote intra-regional trade in goods, the Economic Community of West African States was also intended to reduce food insecurity in the region. However, the “security points”, set up along the trade corridors by the administrative authorities who take bribes, have limited the success of this policy. This corruption is measured not only in bribes – at up to 576 USD per 100 km in Togo in 2017 – but also time loss of more than three hours per 100 km. Putting an end to these practices, which equate to a tax on intra-regional trade, could lead to an increase in the production of food goods of 3% and in consumption by at least 4%. However, coercive policies will not be enough to put an end to these practices that aggravate food insecurity, due primarily to a fleet of trucks that do not comply with road safety and health standards, and to the low and irregular salaries of civil servants. Upstream measures, addressing the economic factors at the origin of corruption, such as the insufficient remuneration of civil servants and the dilapidation of road infrastructure and truck fleets, will be required. Antoine Bouët, Leysa Maty Sall and Fousseini Traoré
>>> |
- What Do We Know About Chinese Industrial Subsidies?
François Chimits - EU Strategic Dependencies: A Long View
Vincent Vicard, Pauline Wibaux
- CEPII Region Profiles: indicators, databases and classifications
Pierre Cotterlaz, Matteo Gagliardi, Carl Grekou, Houssein Guimbard, Laurence Nayman, Erica Perego, Alix de Saint Vaulry, Gianluca Santoni & Deniz Ünal
- Monopsony, Efficiency, and the Regularization of Undocumented Immigrants
George J. Borjas, Anthony Edo - Cheaper and Faster: The Role of Air Services Agreements on Transportation
Charlotte Emlinger, Amélie Guillin - Energy, Inflation and Market Power: Excess Pass-Through in France
Axelle Arquié, Malte Thie - Profit-shifting Frictions and the Geography of Multinational Activity
Alessandro Ferrari, Sébastien Laffitte, Mathieu Parenti, Farid Toubal - Trade and Infrastructure Integration in Africa
Lionel Fontagné, Mathilde Lebrand, Siobhan Murray, Michele Ruta, Gianluca Santoni
- West Africa: Road Harassment Worsens Food Security
Antoine Bouët, Leysa Maty Sall, Fousseini Traoré
The CEPII Profiles have been updated The 2023 update of the interactive CEPII Profiles pages is now online. Numerous indicators illustrate the international integration of countries and regions. For instance, the evolution of Vietnam's trade specialization over two decades reveals an impressive commitment in the manufacturing sector. >>> |
.jpg) The Club of the CEPII hosted a discussion on the recent UNCTAD's "World Investment Report 2023". This annual report is renowned for assessing the latest trends in foreign direct investment around the world, particularly in developing countries. This edition also focuses on the growing and abysmal investment gap facing developing countries in the fight against climate change and proposes priority actions ranging from financing mechanisms to investment policies. >>> |
 The CEPII, LISER and the OECD as well as their partners from the International Migration Economics Chair at Paris School of Economics, the Fondazione Rodolfo De Benedetti, University of Lille (LEM) and University of Luxembourg are jointly organizing the 13th Annual Conference on "Immigration in OECD Countries" on December 11-12, 2023. The conference will examine the economic aspects of international migration in OECD countries by mapping the migratory flows and analyzing their socio-economic determinants and consequences. Topics of interest include, among others, the determinants of immigration to the OECD, migrants’ self-selection, the political economy of immigration, its labor market and public finance effects, as well as migrants and refugees social, political and economic integration. Please submit your paper before 29 September 2023. >>> |
August 2023 issue is out  International Economics, une revue évaluée par un comité des pairs, publie des résultats de recherches dans le domaine de l'économie internationale appliquée. La revue encourage particulièrement les contributions empiriques qui incluent, mais sans s'y limiter, des sujets du commerce international, de la politique commerciale, de la macroéconomie en économies ouverte, de la finance internationale, des taux de change, des politiques financières et monétaires, du développement économique et de la migration. La préparation du numéro d'octobre 2023 est en cours, mais certains articles sont d'ores et déjà disponibles en ligne et entièrement citables. >>> |
- Contact us
- Our other sites
 |
ISSN: 1255-7072
Editorial Director : Antoine BouëtManaging Editor : Evgenia Korotkova






.PNG)