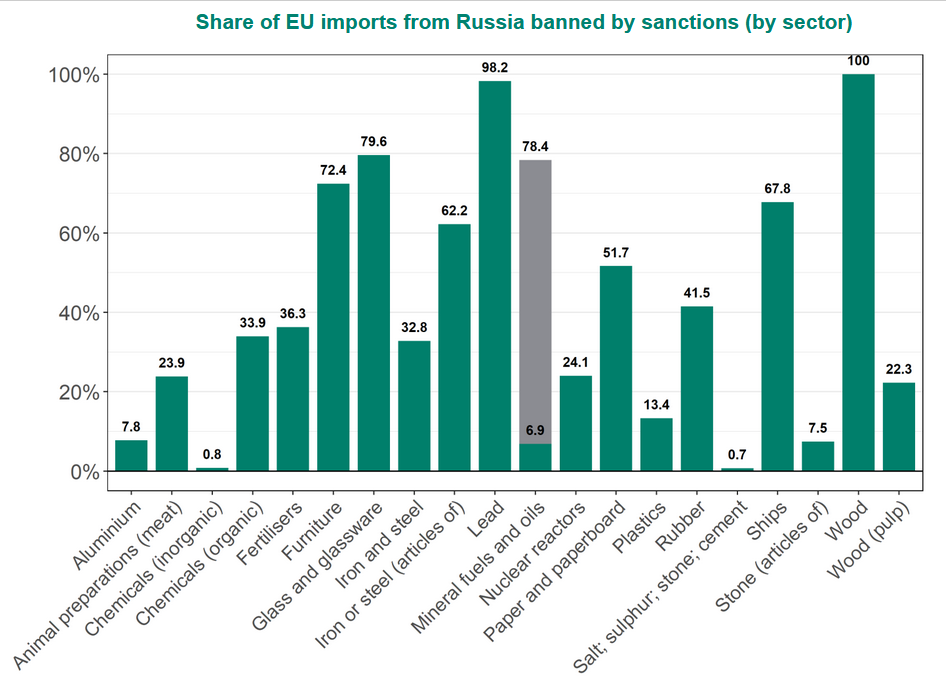
Sanctions against Russia: taking stock four months after the start of the war In 2021, Russia was the EU's fifth largest trading partner, accounting for almost 6% of European trade with the world. The amounts involved are considerable: €258 billion, of which €159 billion are EU imports. Nevertheless, the EU has two advantages over Russia: its significant trade integration and its economic weight. Indeed, while European sanctions (including the sixth package) cover 25% of total Russian exports, they represent only 5% of EU imports. The asymmetry is large. In other words, Russian trade is more dependent on European buyers than European trade is on Russian suppliers. Cecilia Bellora, Kevin Lefebvre and Malte Thie assess the magnitude and the sectors affected by international sanctions using the CEPII's BACI database.
>>> |
Basing upon the 2017 Special Eurobarometer on immigrant integration, the Working paper shows that the population of countries with a relatively high share of immigrants is more likely to consider them as a burden on the welfare system and a crime-prone community. In contrast, natives' opinions on the impact of immigration on culture and the labour market are unrelated to the presence of immigrants. Authors find that the effects of second-generation immigrants on pro-immigrant attitudes toward security and fiscal concerns are positive (as opposed to first-generation immigrants). They find no impact of the immigrants' share on the attitudes of natives supporting far-left or left political parties, while it is the most negative among respondents affiliated with far-right parties. Oscar Barrera, Isabelle Bensidoun, Anthony Edo
>>> |
- Trade sanctions against Russia: taking stock after 100 days of war
Cecilia Bellora, Kevin Lefebvre, Malte Thie
- Second-generation immigrants and native attitudes toward immigrants in Europe
Oscar Barrera, Isabelle Bensidoun, Anthony Edo
Launch of the CEPII's annual flagship publication "World Economy 2023" (in French)
September 7, 2022
Chaos in agrifood trade
Replay
- The Financial Times
The big mistakes of the anti-globalisers
Michel Fouquin - The Conversation
Sanctions against Russia: taking stock four months after the start of the war
Cecilia Bellora, Kevin Lefebvre, Malte Thie - The Conversation
Ukraine Recap: Putin plays historian while the west closes its ranks
CEPII
 A discussion at The Club of the CEPII with Marion Janssen, Christophe Gouel and Vincent Vicard with a specific emphasis on trends and threats in agrifood sector. For the past five years or so, global supply chains have been disrupted by the accumulated consequences of a succession of shocks of increasing intensity: the trade war between China and the United States, COVID and Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The resulting disorder is palpable, but it is difficult to disentangle the different dynamics at work and to anticipate their likely consequences. With the help of two leading experts in the field, we shed light on the current trends in global trade and specific challenges in agricultural trade, and the profound transformation to which they could contribute. A discussion at The Club of the CEPII with Marion Janssen, Christophe Gouel and Vincent Vicard with a specific emphasis on trends and threats in agrifood sector. For the past five years or so, global supply chains have been disrupted by the accumulated consequences of a succession of shocks of increasing intensity: the trade war between China and the United States, COVID and Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The resulting disorder is palpable, but it is difficult to disentangle the different dynamics at work and to anticipate their likely consequences. With the help of two leading experts in the field, we shed light on the current trends in global trade and specific challenges in agricultural trade, and the profound transformation to which they could contribute.>>> |
 On 7 September 2022, the CEPII will be presenting its 2023 edition of "The World Economy". The conference will be held in French. The registration to be open in August. The previous annual publications starting from 2000 are available on our website. On 7 September 2022, the CEPII will be presenting its 2023 edition of "The World Economy". The conference will be held in French. The registration to be open in August. The previous annual publications starting from 2000 are available on our website.>>> |
- Contact us
- Our other sites
 |
ISSN: 1255-7072
Editorial Director : Antoine BouëtManaging Editor : Evgenia Korotkova